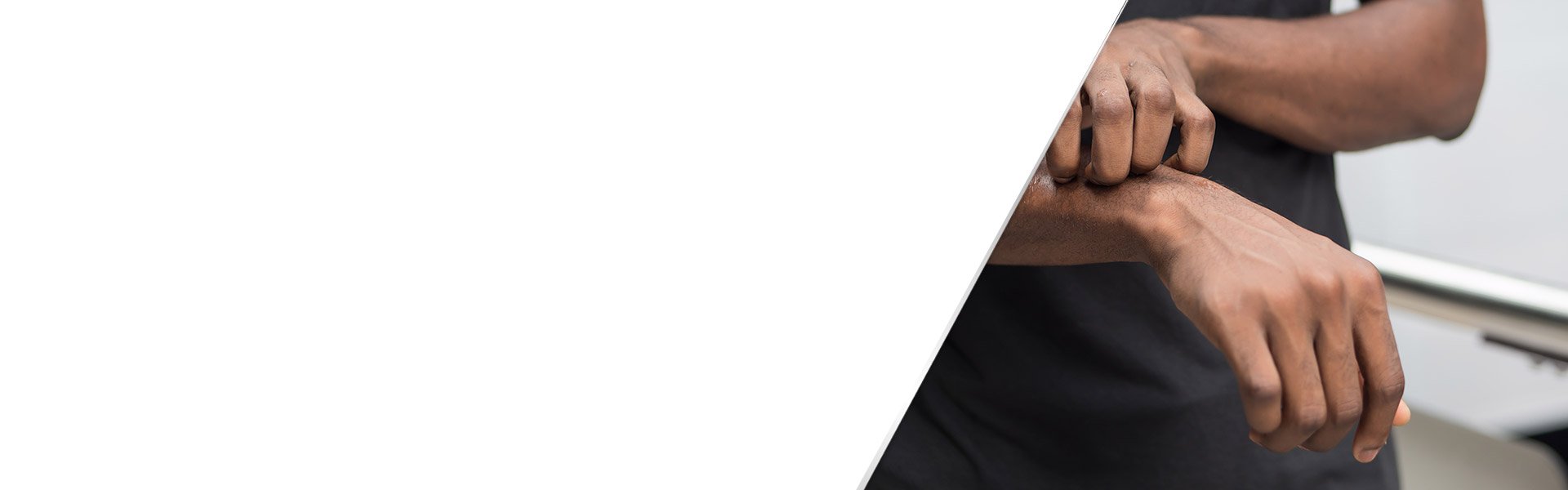
Skin Fungus Treatment and Management
How is Skin Fungus Treated?
Most fungal infections on the skin can be treated with over-the-counter antifungal creams, sprays, or powders. If the infection is more severe, a doctor may prescribe a stronger medication. One effective option is Lamisil Cream for Athlete’s foot or Lamisil Cream for Jock itch, which can help relieve symptoms and clear the infection. (source)
Things you can do at home to treat Skin Fungus
Many mild cases of fungal rashes can be managed at home. It’s important to keep the affected area clean and dry. Applying an antifungal cream, such as Lamisil Cream, can help treat the infection. However, if the rash does not improve, it’s a good idea to consult a healthcare professional.
- Keep the affected area clean and dry: Fungi thrive in moist environments, so it’s important to regularly clean and thoroughly dry the infected skin each day.
- Use over-the-counter antifungal creams, sprays, or powders: Products like Lamisil Cream can cure most fungal infections. Always follow the instructions provided.
Medications Used to Treat Fungal Infections on The Skin
Topical antifungal treatments, like Lamisil Cream, are commonly used to treat fungal infections on the skin. In some cases, oral antifungal medications may be prescribed if the infection is more widespread or resistant to topical treatments.